Logical & Physical Structure of a Hard Disk
In this article explain Logical & Physical Structure of a Hard Disk there components uses.
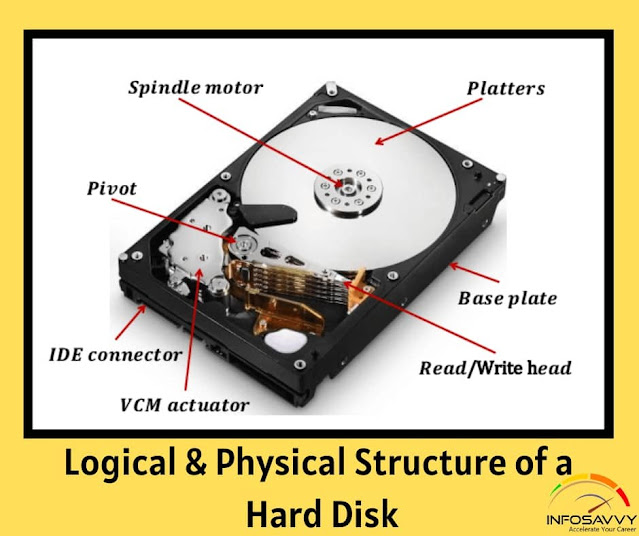
Physical Structure of a Hard Disk
The main components of hard disk drive are:
- Platters: These are disk like structures present on the hard disk, stacked one above the other and store the data
- Head: It is a device present on the arm of the hard drive that reads or writes data on the magnetic platters, mounted on the surface of the drive
- Spindle: It is the spinning shaft on which holds the platters in a fixed position such that it is feasible for the read/write arms to get the data on the disks
- Actuator: It is a device, consisting of the read-write head that moves over the hard disk con to save or retrieve information
- Cylinder These are the circular tracks present on the platters of the disk drive at equal distances from the center
Related Product : Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator | CHFI
Physical Structure of a Hard Disk (Cont’d)
A hard disk contains a stack of platters, circular metal disks that are mounted inside the hard disk drive and coated with magnetic material, sealed in a metal case or unit. Fixed in a horizontal or vertical position, the hard disk has electromagnetic read or write heads above and below the platters. The surface of the disk consists of a number of concentric rings called as tracks; each of these tracks has smaller partitions called disk blocks. The size of each disk block is 512 bytes (0.5 KB). The track numbering starts with zero. When the platter rotates, the heads record data in tracks. A 3.5-inch hard disk can contain about thousand tracks.
The spindle holds the platters in a fixed position such that it is feasible for the read/write arms to get the data on the disks. These platters rotate at a constant speed while the drive head, positioned close to the center of the disk, reads the data slowly from the surface of the disk compared to the outer edges of the disk. To maintain integrity of data, the head is reading at a particular period of time from any drive head position. The tracks at the outer edges of the disk have less densely populated sectors compared to the tracks close to the center of the disk.
The disk fills the space based on a standard plan. One side of the first platter contains space, reserved for hardware track-positioning information which is not available to the operating system. The disk controller uses the track-positioning information to place the drive heads in the correct sector position.
The hard disk records the data using the zoned bit recording technique, also known as multiple zone recording. This method combines the areas on the hard disk together as zones, depending on the distance from the center of the disk. A zone contains a certain number of sectors per track.
Calculation of data density of disk drives is done in the following terms:
- Track density: Refers to the number of tracks in a hard disk
- Area density: Area density is the platters’ storage capacity in bits per square inch
- Bit density: It is bits per unit length of track
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com



Comments
Post a Comment